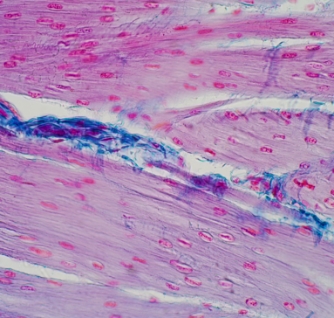
Use of a digital morphometry tool for histological assessment in an Elastase-induced COPD model in mice
Loeb E¹, Zuckerman A¹, Margalit R², Alagem N ³, Sagiv Y ³. ¹Patho-Logica, Golda Meir Street 7, Scientific Park, Ness-Ziona, Israel. ²Science In Action, Sapir Street 5, Scientific park, Ness-Ziona, Israel. ³ Kamada Ltd, Holzman 2, Scientific Park, Rehovot, Israel
Introduction:
The Elastase-induced COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) mouse model is well-known for emphysema studies. Following administration of test drug, Elastase is instilled intratracheally once a week for four weeks to induce COPD. Lungs are harvested, fixed, and stained for histological evaluation. The H&E-stained slides are analyzed using a digital morphometry tool as applied to the analysis of representative pictures of the affected lung parts.
Aim:
The objective of this study was to develop a reliable quantitative tool for assessing the degree of alveolar loss and rupture damage in treated vs. control lungs of elastase-induced COPD in mice as parameters for the assessment of a treatment effect.
Materials and Methods:
- Anesthetized mice received weekly intratracheal instillations of 20 µL Test Item.
- 24 hours after each dose, 0.2U PPE in 20 µL saline was instilled.
- At the end of weeks 2, 3 & 4, five mice were sacrificed for histology.
- Lungs were fixed in 4% Formaldehyde using intra- and extra-bronchial fixation (gravitation method).
- 5-µm-thick paraffin sections were cut and H&E stained.
- Representative pictures were taken in affected areas (4 fields per lung) using 4X objective magnification
Digital morphometry analysis:
Image analysis was performed using “Image Pro Plus” Version 6.3 (Media Cybernetics, US). From each histological slide, four pictures were taken and sent for digital analysis.
Protocol:
- 1. Spatial calibration was applied (marked calibration).
- 2. Area of Interest (AOI) selection was chosen.
- 3. Threshold selection was based on HSI color system (Hue, Saturation and Intensity).
- 4. Intensity of 96-255 grey levels was depicted to show the void spaces.
- The calibrated parameters of Area and Perimeter were measured and used for creating statistical data.
Table 1: Results of morphometry, digital evaluation of lung emphysema.
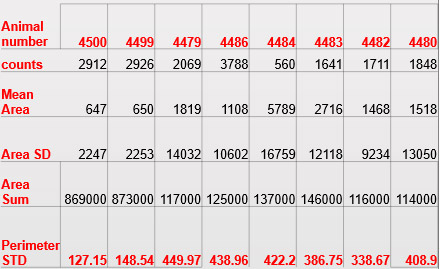

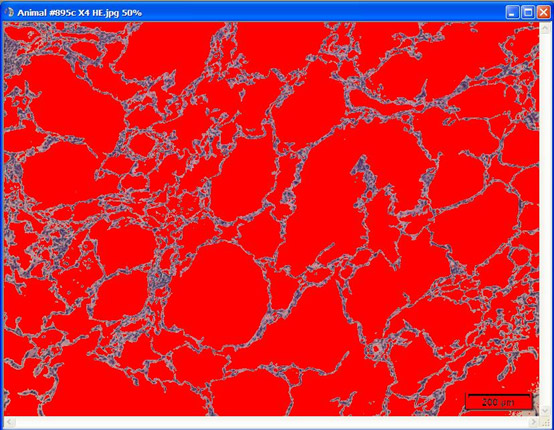
Figure 1: Illustration of a threshold image measurement of alveolar spaces in the Lung, shown in red X4 H&E.

Results:
- Morphometric quantification shows clear differences in area counts, mean and sum when comparing healthy and affected lungs through accurate comparison between affected lungs (Table 1).
- SD shows greater variation in the measurement of the affected lungs compared to the healthy lungs.
- Areas of air were quantified using a rigid threshold (Fig. 1)
- We extract the numbers from the histological image and show them in a graph for comparative means (Fig. 2)
- Area / Perimeter provide a good index for emphysema quantification (Fig. 3)
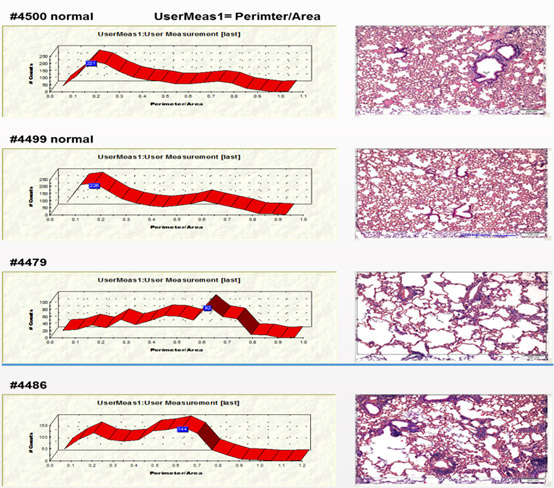

Figure 2. Representative pictures of two normal and two affected lungs with different graph profiles
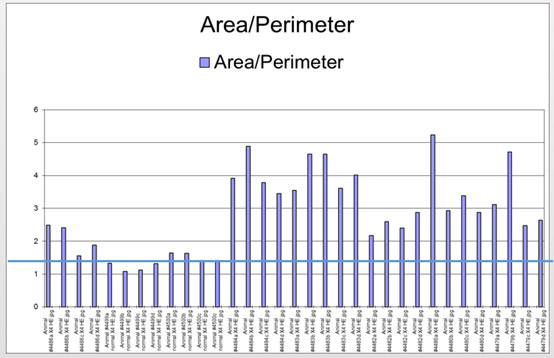

Figure 3. Summary of x4-fold measurements per animal area / perimeter.
Summary and Conclusions:
We have developed a very accurate and useful tool for the quantification of alveolar loss and rupture damage in a mouse emphysema model. This morphometry technology enables a quantification of the comparison of different treatments effects in this model, and should be applicable to other models where key morphological features can be quantified.
References:
- Cruz F. F., Antunes M. A., Abreu S. C., Fujisaki L. C., Silva J. D., Xisto D. G., et al. . (2012). Protective effects of bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy on lung and heart in an elastase-induced emphysema model. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 182, 26–36.
- Weibel E. R. (1990). Morphometry: stereological theory and practical methods, in Models of Lung Disease-Microscopy and Structural Methods, eds Gil J., editor. (New York, NY: Marcel Dekker; ), 199–247