CNS models in rodents: What can you expect from your experimental pathologist?
Dr. Emmanuel Loeb
Introduction
Three major parameters are important for accurate histopathological results in CNS models:
- Tissue preparation for representative lesion exposure and analysis.
- Choice of histological tools for measuring your desired end points.
- Accuracy of the analytical process.
An example of a Stroke (MCAO) study in a rat model.
Tissue preparation for representative lesion exposure and analysis
Tissue harvest and fixation:
- For fluorescence analysis, performance of brain perfusion prior to brain / spinal cord harvest.
- Harvesting the organs by valid procedures to avoid artifacts.
- Fixation of organs in 4% PFA and storage at 4°C.
- Sample labeling and administration.
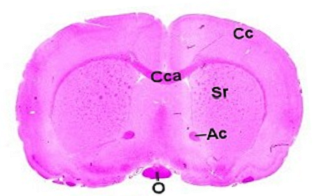

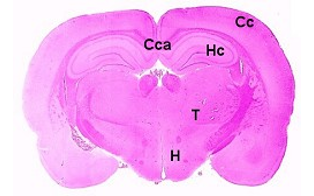

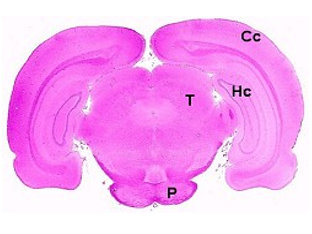
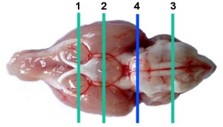
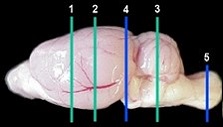
Brain, localization 1, striatum Brain, localization 2, dorsal hippocampus
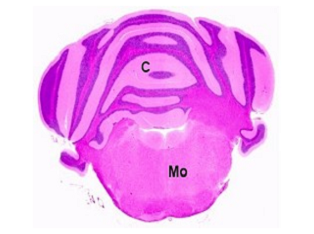


Brain, localization 3, cerebellum and Brain, optional localization 4,
medulla oblongata cerebrum and pons.
Abbreviations used in the above images:
Ac: anterior commissure, C: cerebellum, Cc: cerebral cortex, Cca: corpus callosum, H: hypothalamus,
Hc: hippocampus, Mo: medulla oblongata, O: optic chiasm, P: pons, Sr: striatum, T: thalamus


Tissue preparation and trimming
- Preparation of the appropriate crosssection in the organ for representative exposure.
- Assurance of having the relevant anatomical structure in the same position for all samples.
- Use of brain matrix system for this purpose.
- Replacement of all crosssections for all animals in the same block position.
Tissue processing and slide production
- Use of highstandard tissue processor with an accurate program for each tissue type.
- Highly trained technician for block production and sectioning.
- Production of topquality histological slides for interpretation and analysis.
The choice of histological tools for measuring your desired endpoints
Common stains and IHC markers used in CNS models
Choice of the best tool depends on the scientific aim and the relevant endpoint.
- H&E: Used for general morphology and quantification of lesions.
- Demyelination: MBP for myelin, Olig2 for total oligodendrocytes, NG2 for young oligodendrocytes.
- GFAP: for Astrocytes
- Iba1: For Microglia
- NeuN:For neuron count
- ChAT:For motor neurons
- NF: For total neuron fibers
- TH: For Dopamine/norepinephrine producing cells (PD)
- betaAmyloid, TauP: For Protein products (AD)
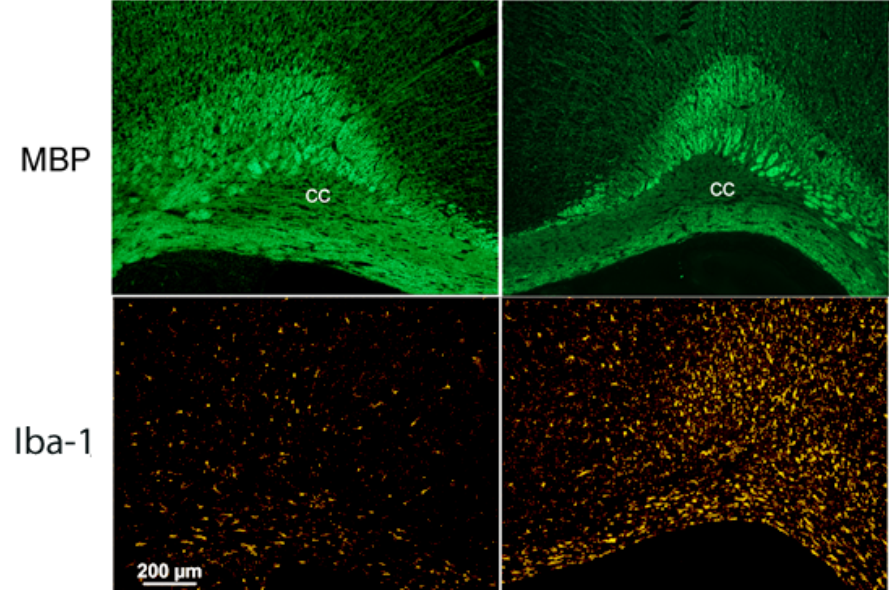

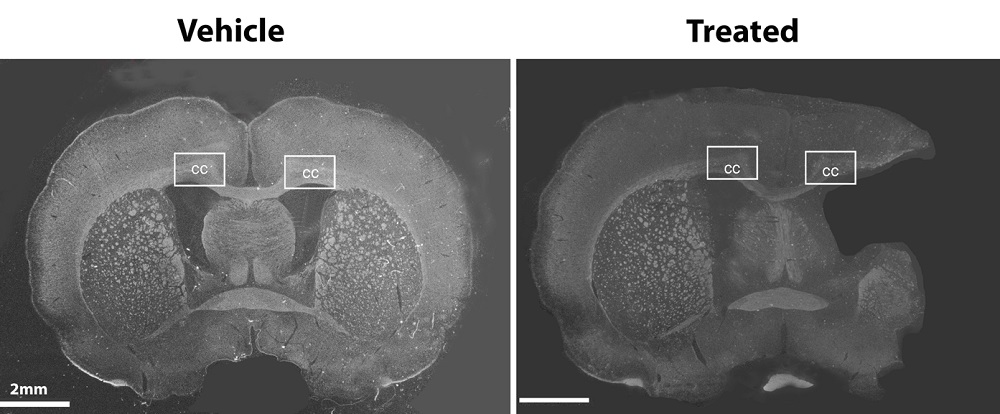
Stroke (MCAO) study in a rat model. Left intact hemisphere, right affected side. Note the loss of myelin and increase of microglia.
Accuracy of the analytical process
Analytical process
- Doubleblind examination by an experienced pathologist
- Semiquantitative vs. morphometry analysis
- Image analysis•Wholeslide scan (digital slides)
- Advanced digital analysis•Accurate data
- Avoid bias between pathologists
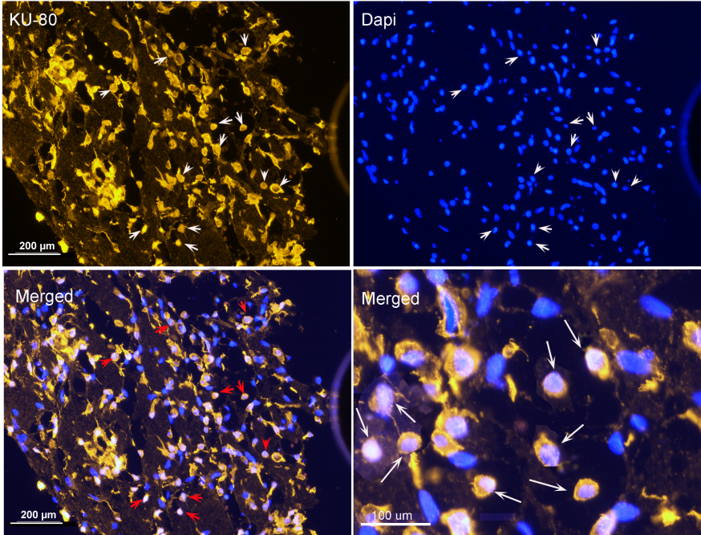

Ku80 for human cells in treated brain infarct in a rat (MCAO) model.
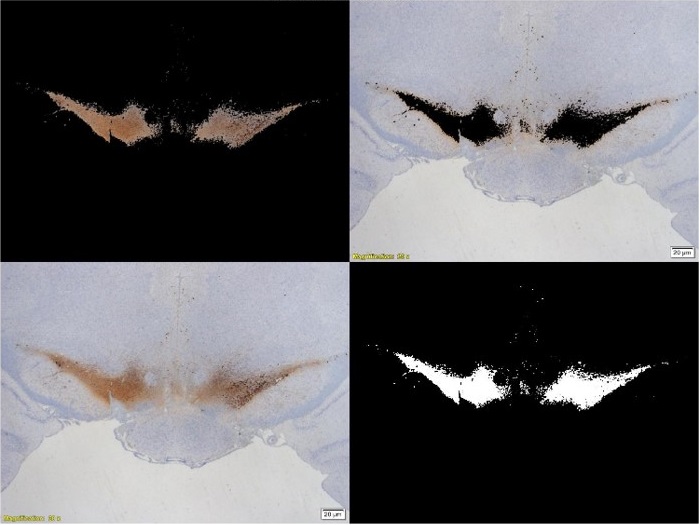

TH (Tyrosine Hydroxylase) measurements in the SNc (substantia Nigra pars Compacta).
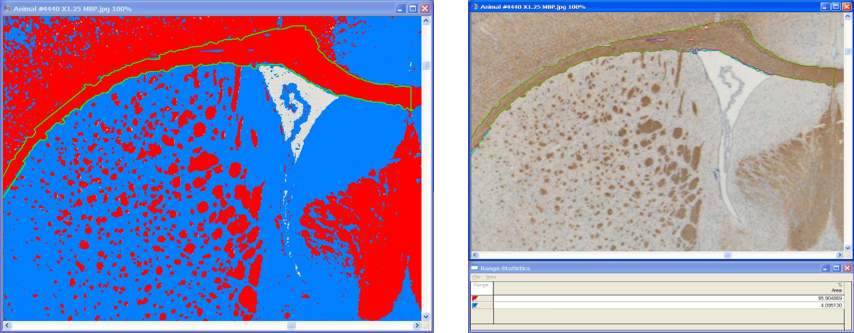

MBP quantification using segmentation analysis.